China has ascended as the global leader in green and low-carbon technology patents, signaling a major shift in the realm of sustainable innovation. According to a research report released on July 28 by China’s leading intellectual property regulator, Chinese applicants had 101,000 green and low-carbon patent applications published in 2023. This number is nearly five times greater than Japan, which holds the second spot, and significantly surpasses South Korea, the United States, and Germany.
This figure marks a 20.1% year-over-year increase, exceeding the global average growth rate by 7.1 percentage points. The report indicates that China has greatly accelerated the green and low-carbon patent sector, both in terms of the number of published applications and granted patents, while also innovating across all areas of green and low-carbon technology.
Rise in Chinese Green Patent Applications and Grants
Between 2016 and 2023, Chinese patentees sustained an impressive annual growth rate of 12.3%, with a total of 555,000 published applications worldwide. This is nearly three times the number of applications from Japan, which had 200,000. The United States, South Korea, and Germany followed with 157,000, 108,000, and 74,000 respectively. Collectively, these five leading countries accounted for 85.7% of the global total applications.
During the same period, the number of green patents granted to Chinese applicants reached 230,000, representing 35.1% of the total patents granted in the five major patenting regions. Japan, Europe, the United States, and South Korea followed in succession.
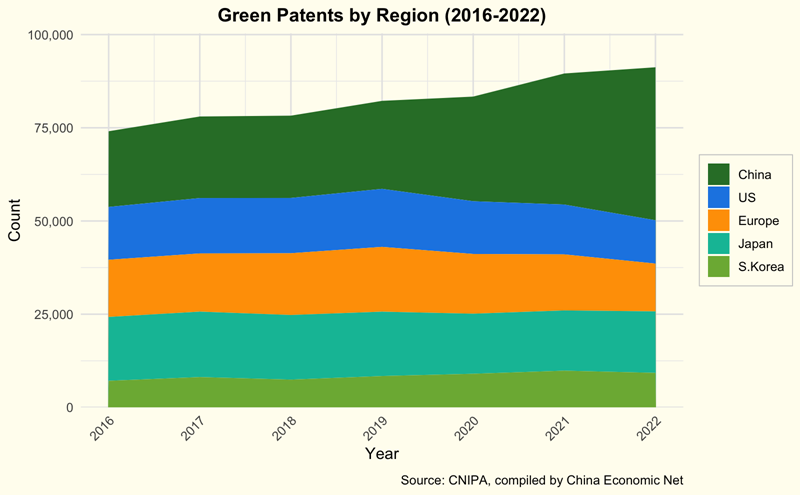
The report highlighted that in 2023, 82.5% of global patent applications were published by the patent offices of China, the U.S., Europe, Japan, and South Korea. Leading the charge, the China National Intellectual Property Administration (CNIPA) published the largest share with 97,000 green patents, reflecting a 14.5% increase from the previous year. Additionally, 45,000 green patents were granted, an 8% rise from 2022. These numbers account for over half of the global totals, with worldwide green patent applications reaching 193,000 and grants totaling 95,000 in the same year.
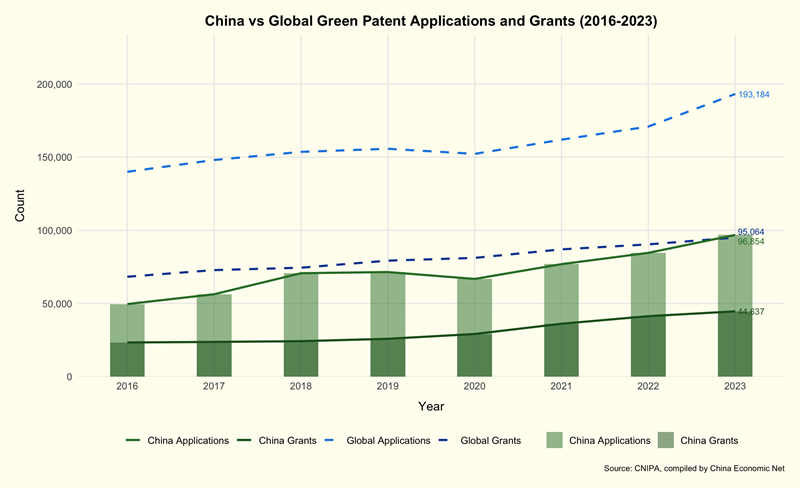
From 2016 to 2023, the number of green patent applications published in China reached 573,000, growing at an average annual rate of 10.0%, outpacing China’s overall patent growth rate of 7.8%. During this period, China was granted 249,000 green patents. This growth contrasts with the declining rates seen in several green technology areas in traditional innovation powerhouses like the U.S., Japan, and Germany.
Notably, 13 out of the top 50 patentees during the 2016-2023 period are based in China. These include nine companies, such as the State Grid (ranked 3rd) and Contemporary Amperex Technology Co., Limited (CATL) (ranked 26th), and four universities and research institutes, including the Chinese Academy of Sciences (ranked 9th).
Increase in Clean Energy Patents
The report indicated that China has also taken the lead in all five sectors of green technology patents: fossil fuel decarbonization, energy conservation and recycling, clean energy, energy storage, and greenhouse gas capture, utilization, and storage.
From 2016 to 2023, patents related to energy saving and recycling made up the largest share, with 211,000 (34.9%) of China’s 573,000 published green patent applications. This was followed by energy storage (163,000), clean energy (124,000), fossil fuel decarbonization (69,000), and greenhouse gas capture, utilization, and storage (39,000).
It is noteworthy that energy storage applications surged starting in 2016, topping the chart in 2023 with a 19.3% average annual growth during the period, breaking the dominance of energy saving and recycling from 2016 to 2022. Clean energy patents also showed stable growth, with an average annual growth of 8.7%.
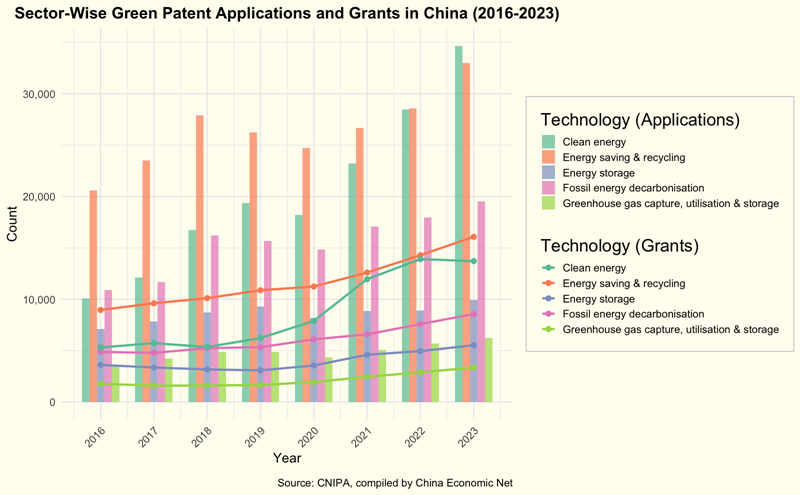
Green patent grants in China followed a similar trend over the same period. From 2016 to 2023, energy saving and recycling grants reached 94,000, comprising 35.8% of the 248,000 total grants. This was followed by energy storage, clean energy, fossil fuel decarbonization, and greenhouse gas capture, utilization, and storage. Notably, energy storage grants experienced the most significant growth, with an average annual rate of 15.9%.
In the clean energy sector, solar energy and hydrogen energy have shown considerable promise, each accumulating over 10,000 patents between 2016 and 2023. Solar energy led the way with 18,000 patents (34.8% of clean energy patents), while hydrogen energy secured 12,000 patents (23.3%).
On a global scale, Chinese patentees also led in all five sectors. The cumulative published applications and grants for each category surpassed those of traditional innovators, including the U.S., Europe, Japan, and South Korea. The proportion of published applications from Chinese entities in energy saving and recycling, energy storage, and clean energy surged from 34.6%, 25.9%, and 29.5% respectively in 2016 to 59.4%, 48.3%, and 49.6% of the global total in 2023.
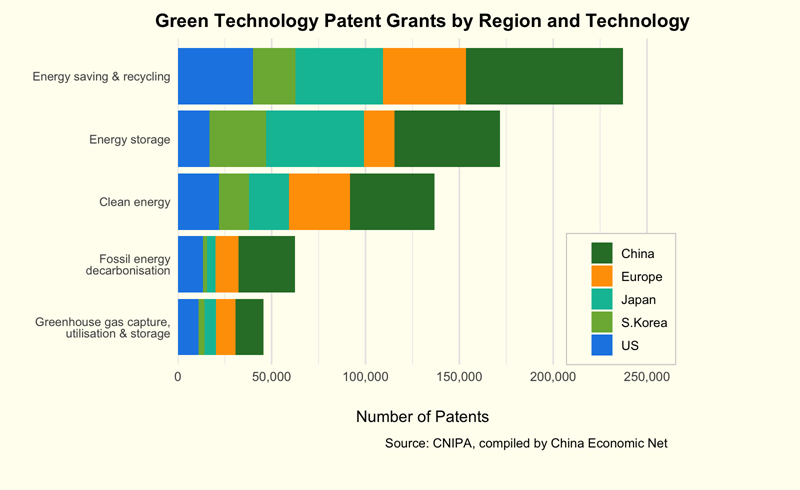
Similarly, the share of grants in the three areas for Chinese patentees was 25.6%, 23.5%, and 20.7% of the total respectively in 2016, growing to 48.9%, 39.9%, and 42.4% respectively in 2023.
It’s important to highlight that published patent applications represent only a subset of the total patent applications.
As the world faces the urgent need for sustainable solutions, attention will be focused on how China utilizes its expanding green patent portfolio to tackle global environmental challenges in the coming years.



